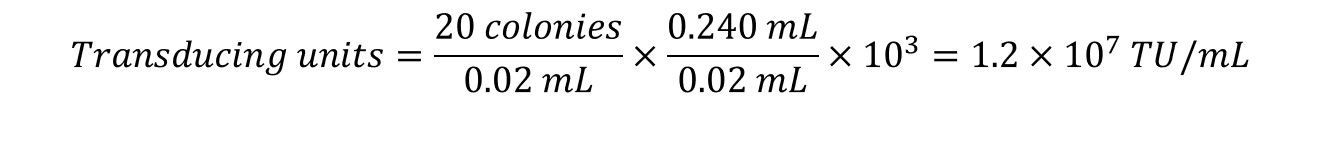Titering Transducing Units (TU/mL)
This protocol is the routine procedure for titering filamentous phage to determine the transducing units (TU) and is essential in micropanning experiments. Quantifying TU is not a highly reproducible method of determining phage numbers, but rather determines the number of infective phage. Phage particles can be more accurately quantified by measuring the amount of phage virions (virions/mL). The E. coli host strain in this protocol is K91BluKan. However, any E. coli cell displaying the F pilus (Hfr, F+ or F´ “males”) can be used.
This protocol is based on and modified from the The Laboratory of George P. Smith at the University of Missouri. The protocols were previously hosted by http://www.biosci.missouri.edu/smithgp/
Reagents
Note: This protocol describes the amplification of filamentous phage based on the Fd-tet vector (tetracycline resistant) and uses K91BluKan E. coli cells (kanamycin resistant) that are cultured in NZY medium. The protocol can be modified to accommodate other phage variants and E. coli strains when taking into account their optimal medium and antibiotic resistance.
- NZY medium
- E. coli K91BluKan
- Terrific broth
- TBS gelatin
- Kanamycin
- Tetracycline
- NZY agar
Protocol
E. coli cultures
1. Inoculate 2 mL of NZY medium with 100 µg/mL kanamycin with K91BluKan E. coli and incubate overnight at 250 rpm at 37ºC.
2. Use 100 µL of the overnight culture to inoculate 10 mL terrific broth in a 125 mL flask. Shake at 250 rpm and 37ºC until the culture gets turbid.
3. Begin reading the OD600 of 1/10 dilutions. When the OD600 of a 1/10 dilution reaches 0.125-0.25, slow the shaking down to 50 rpm to allow sheared F-pili to regenerate. Use these cells for titering within 1 h.
Analytical Titering
1. In a microtiter or 96-well plate, make serial 10-fold dilutions by adding 2.2 µL of the phage solution to 20 µL TBS gelatin diluent.
2. Add 20 µL of the E. coli culture in terrific broth from above and incubate at room temperature without shaking for 10 min to allow infection.
3. Add 200 µL of cell medium supplemented with 0.2 µg/mL tetracycline and incubate for 30 min at 37C°. This is the gene expression period, during which the antibiotic resistance gene on the incoming phage has a chance to be expressed before the infected cells are challenged with a high concentration of the antibiotic.
i. If using a different strain of E.coli, use an antibiotic concentration equivalent to 0.01X.
4. Spot 20 µL from each well in duplicate onto preferably a square dish with NZY/agar containing 40 µg/mL tetracycline and 100 µg/ml kanamycin. Let the spots dry and incubate the plate upside down at 37°C for 12 h to overnight.
5. Count the colonies in each spot and complete the calculations:
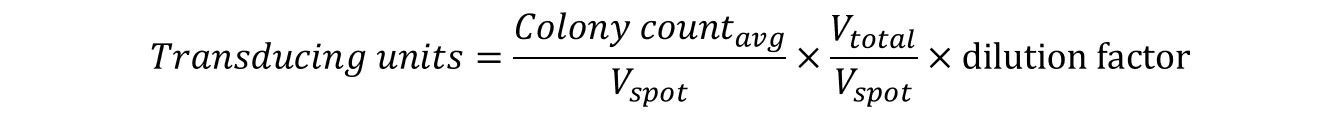
Example: 20 µL from the103 dilution was spotted in duplicate on NZY/agar plates. The colonies from each spot was counted and found to be 18 and 22. The TU/mL was calculated as follows: