Quantifying Phage Virions
This protocol is the routine procedure for the quantification of filamentous phage particles. The absorbance of phage DNA and protein is measured spectrophotometrically and used to calculate virions/mL (V/mL).
This protocol is based on and modified from the The Laboratory of George P. Smith at the University of Missouri. The protocols were previously hosted by http://www.biosci.missouri.edu/smithgp/
Protocol
Filamentous phages contain approximately six times more protein than DNA. Thus, the protein contributes substantially to the absorption spectrum accounting for a broad plateau at 260–280 nm with a shallow maximum at 269 nm. The calculation of the phage concentration in virions/mL (V/mL) is based on Day et al., 1978 and is as follows:
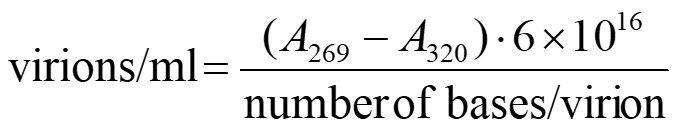
Subtracting A320, a wavelength where there is little light absorption from phage chromophores, is meant to correct crudely for light scattering from phage particles and non-phage particulate contaminants.
Example calculation of a solution of phage clones with a genome of 9312 bases:
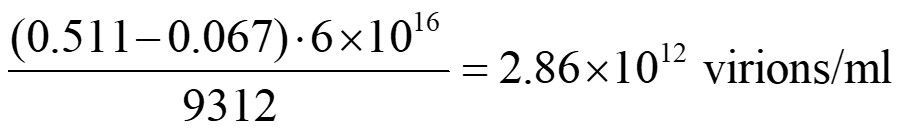
Tips & Tricks
- For the most accurate results use a phage-free solution as a blank (background) measurement.
